Have you ever had such a situation—— Sometimes I feel I can’t hear clearly; Sometimes I feel I can hear clearly.
Listening is good and bad, which makes you confused. In a trance, you may think that the bad hearing during that period of time is an illusion.
So how does this kind of hearing situation happen?

What are the causes of sudden good and bad hearing?
High-intensity noise environment
If you stay in a noisy environment for a certain period of time, your hearing may change. This phenomenon is called temporary threshold shift (TTS), that is, people’s hearing threshold has changed temporarily.
Simply put, your ears think that the normal hearing value has been raised. When leaving this kind of strong noise environment, the ear will begin to recover slowly and the hearing threshold will also recover gradually.
However, it should be noted that if you are in a strong noise environment for a long time, the temporary threshold shift will become a permanent threshold shift.
Cerumen embolism
Cerumen is what we commonly call “earwax”. When accumulated too much, blocking the external auditory canal may also lead to “persistent” hearing loss.
In this case, it is often necessary to completely remove the cerumen in order to restore the original hearing. But in some cases, cerumen embolism may also make your hearing better and worse.
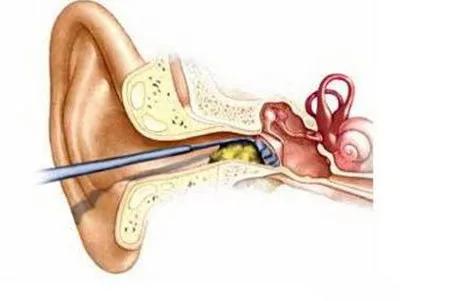
Because the sound will change constantly in the transmission process of the external auditory canal due to the blockage of cerumen, resulting in good and bad hearing.
Fluctuating hearing loss
It is not common in general patients, but it sometimes occurs in patients with Meniere’s disease.
One of the characteristics of Meniere’s disease is the fluctuating change of hearing, which usually occurs in one ear. At this time, the hearing of the affected ear will fluctuate over a period of time.
But this change is likely to last for days, not minutes or hours.
Eustachian tube dysfunction
The eustachian tube is a small tube connecting the middle ear tympanic chamber to the back of the nose. The task of this tube is to balance the air pressure outside the ear and the middle ear tympanic chamber by opening and closing.
Normally, the eustachian tube is closed and has a weak sense of existence. The eustachian tube is open only when people swallow, yawn, and sneeze, which is used to balance the pressure in the middle ear cavity and the external atmospheric pressure.
Therefore, when we fly, we can relieve the ear blockage caused by the frequent change of air pressure by swallowing.
However, if your eustachian tube “strikes”, your ears will feel blocked and your hearing will be affected.
How can we protect our hearing?
Avoid noise damage to hearing.
If the elderly are exposed to noise such as machine roar and human noise for a long time, their hearing is easy to fatigue, and the micro blood vessels of the inner ear are in a spasm state, resulting in insufficient blood supply to the inner ear, their hearing will decline rapidly, and even noise deafness.
Therefore, earplugs or earmuffs can be prepared for the elderly to reduce noise hazards.
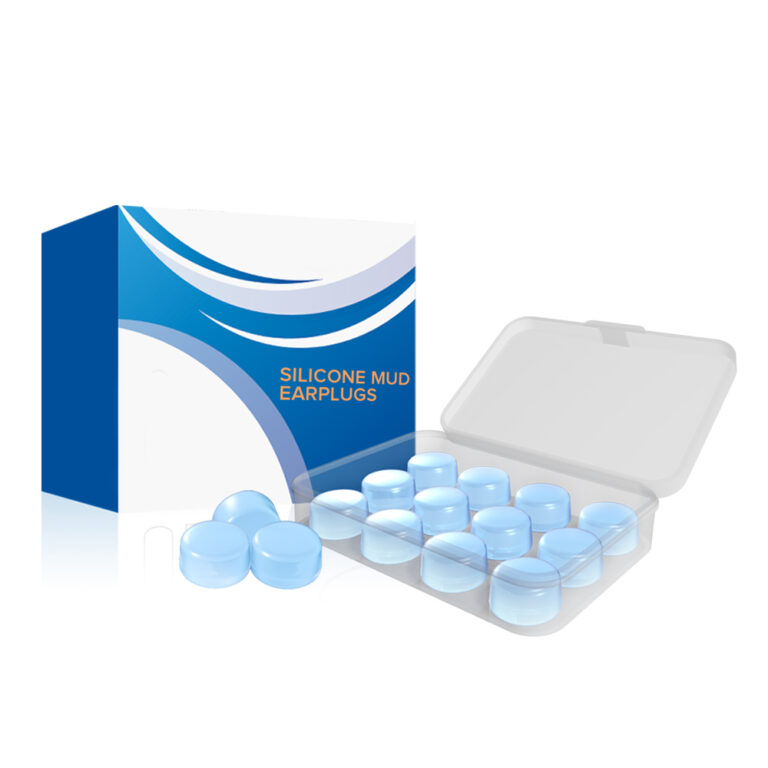

Prevent ear canal infection.
Avoid water in the ear canal during bathing and swimming. You can use silicone mud earplugs to prevent water from entering.
Do not dig your ears blindly. If your ears itch, you can wash them with an alcohol cotton swab; In case of cold, rhinitis, or sinusitis, anti-inflammatory nose drops should be used to keep nasal breathing unobstructed and avoid ear canal infection through the pharyngeal tube.
Use drugs with caution.
See the drug instructions clearly, prohibit, use with caution, useless, and do not use drugs that are harmful to the “auditory nerve” for a long time, especially streptomycin and aminoglycoside antibiotics.
Often massage the ears.
There are a large number of acupoints in the ear, which are closely related to internal organs. It is quite beneficial to massage the ear regularly, three times a day.
